Study Links Thumb Length to Brain Size and Cognition
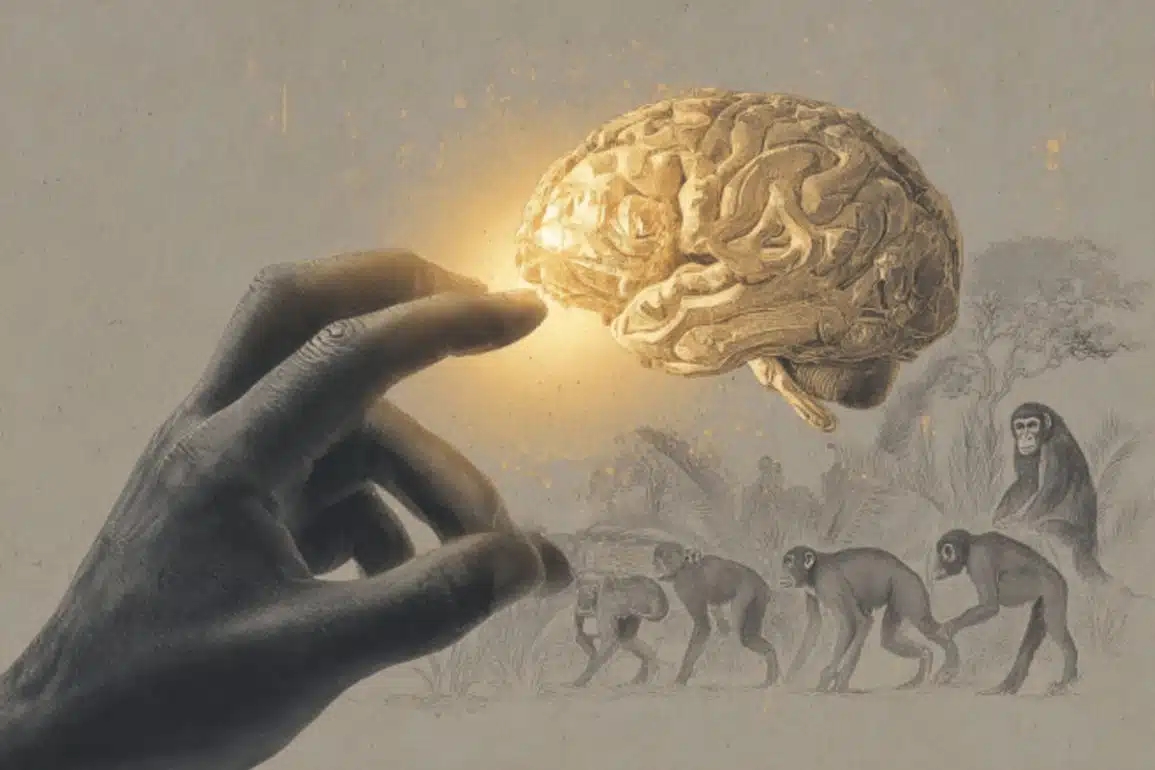
New research reveals that primates with longer thumbs tend to have larger brains, suggesting that manual dexterity and brain evolution developed together. The study analyzed 94 living and extinct primate species and found a consistent link between thumb length and brain size. Surprisingly, the growth was tied to the neocortex — the region linked to higher thinking — rather than the cerebellum, which controls movement. This provides the first direct evidence that the evolution of precise gripping and cognition were tightly intertwined. ….[READ]
Publisher: Source link