Skin-to-Skin Contact Boosts Brain Development
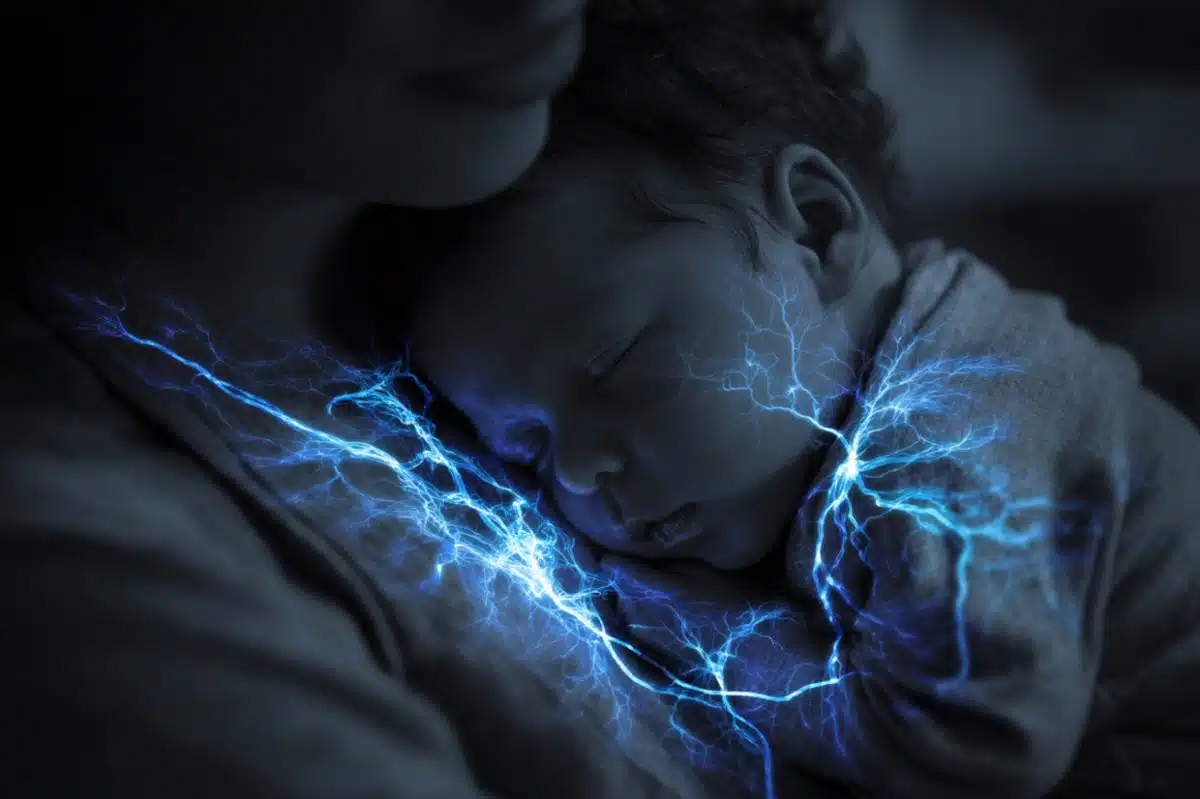
Very preterm infants who received more skin-to-skin contact during their hospital stay showed stronger development in brain regions tied to stress and emotional regulation. Brain scans revealed that longer skin-to-skin sessions were linked to changes in white matter pathways that support attention, memory, and emotional health. These associations held even after accounting for socioeconomic status and other factors. The findings suggest that caregiving experiences in the earliest weeks of life may influence long-term brain development. ….[READ]
Publisher: Source link